First of all, congratulations on taking up web development! Whether you are a novice, hoping to get into the world of web development or an experienced developer, keen to improve your skills, I've got just the right content for you. In this blog, you'll know everything you need, about HTML. Also, keep in mind that NO developer knows EVERYTHING! You will have to keep learning new stuff as you work on new projects with different requirements.
What is HTML?
HTML is used to lay the basic structure of a webpage. CSS is used to make a webpage visually appealing and JavaScript to add functionality to it. Let's learn HTML, for now.
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. Here, Hypertext means that the document contains links that allow the reader to jump to other places in the document or to another document altogether. A Markup Language is a way that computers speak to each other to process and present the text.
Basic structure of an HTML document
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> A basic HTML Document </title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> HEY!! </h1>
<p> YES, Not HELLO WORLD, just HEY! </p>
</body>
</html>
This sequence cannot be changed. Here,<!Doctype html> specifies the language used which is HTML5.<html signal the beginning of HTML code.<head> contains metadata of the webpage.<meta> contains information such as title, character encoding, etc.<body> contains the visible part of a webpage.<h1> defines a heading.<p> defines a paragraph.
Now that you know the basic structure, Let's learn about other tags.
A. Tags
a. Heading
In HTML, a heading is defined by <h1>...</h1> tag.
According to visual hierarchy, there are 6 heading tags from <h1> to <h6>.
Example:
<h1> Heading 1 </h1>
<h2> Heading 2 </h2>
<h3> Heading 3 </h3>
<h4> Heading 4 </h4>
<h5> Heading 5 </h5>
<h6> Heading 6 </h6>
Output:

b. Paragraph
In HTML, a paragraph is defined by <p>...</p> tag.
Example:
<p> This is a paragraph </p>
Output:

c. Link
In HTML, a link can be given by using <a>...</a> tag.
Example:
<a href="www.instagram.com"> Click here</a>
We will learn about href in attributes.
Output:

d. Image
IN HTML, an image can be embedded by using <img> tag.
Example:
<img src="girl.png" alt="A girl">
We will learn about src and alt in attributes.
Output:

e. Lists
IN HTML, a list can be made either by <ol>...</ol> or <ul>...</ul> tag.<ol>...</ol> makes an ordered list.<ul>...</ul> makes an unordered list.
The list items are given in <li>...</li> tag.
Example:
<ol>
<li> One </li>
<li> Two </li>
<li> Three </li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li> Milk </li>
<li> Tea </li>
<li> Coffee </li>
</ul>
Output:
- One
- Two
- Three
- Milk
- Tea
- Coffee
f. Line break
In HTML, an empty element inserts a line break using <br>.
Example:
<p> We can create a line break using <br> tag in paragraphs. <p>
Output:

g. Horizontal Rule
IN HTML, a horizontal rule can be created using the <hr> tag.
Example:
<p> We can create a line break using <br> tag in paragraphs. <p><hr>
Here is another horizontal rule. <hr>
Output:

NOTE : Few tags like
<img>, <hr>, <br>do not have an end tag. You can learn other tags as you develop new webapages. These are all the basic tags you should know. Let's see attributes.
B. Attribute
All HTML elements can have attributes. Attributes provide additional information about elements. Attributes are always specified in the start tag and usually come in name/value pairs like name="value".
a. The href attribute
href means hyperlink reference.
It defines the URL of the link provided in the <a> tag.
Example:
<a href="www.google.com"> Google </a>
Here, href is defined inside the start tag, followed by a URL.
b. The src attribute
src means source.
It defines the path of an image.
Example:
<img src="flower.png">
Here, src is defined inside the start tag, followed by a path to the image.
c. The alt attribute
alt means alternate (text).
It defines an alternative to showcase, in case the image isn't loaded due to network issues or an incorrect path.
Example:
<img src="flower.png" alt="A flower image">
Here, alt is defined inside the start tag, followed by an alternate text.
d. The width and height attribute
The width attribute defines the width of an image and
the height attribute defines the height.
Example:
<img src="flower.png" alt="A flower image" width="200" height="200" >
The dimensions of an image or any other element are usually given in pixels.
e. The style attribute
The style attribute enhances the appearance of the element. Example:
<h1 style = "color: red"> A red Heading </h1>
<p style = "font-size: 14; color: blue"> A paragraph with
small font and blue text </h1>
<p style = " color: blue; background-color: yellow"> A paragraph with
blue text and yellow background </p>
Output:

C. Formatting
a. Bold
To make a text bold, we can use either <b>...</b> tag or <strong>...</strong> tag.
Example:
<p> A <b> bold </b> text. </p>
Output: A bold text.
b. Italic
To make a text italic, we can use either <i>...</i> tag or <em>...</em> tag.
Example:
<p> An <em> italic <em> text. </p>
Output: An italic text.
c. Subscript and superscript
To write a subscript, we can use the<sub>...</sub> tag.
To write a superscript, we can use<sup>...</sup> tag.
Example:
<p> H <sub> 2 </sub> O, CO <sub> 2 </sub></p>
<p> 2 <sup> 3 </sup> = 8, 3 <sup> 2 </sup> = 9 </p>
Output:
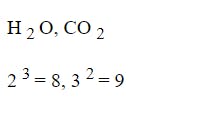
d. Delete
To delete a text, we can either use<del>...</del> tag
or <strike>...</strike> tag.
Example:
<p> Rs. <del>999</del> 699. </p>
Output:
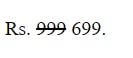
e. Highlight
To highlight a text, we can use the<mark>...</mark> tag.
Example:
<p> Rs. <del>999</del> <mark> 699. <mark> </p>
Output:
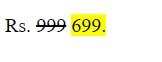
Summary:
| Sr. No. | Tag / Atribute | Description |
| 1 | <h1>...</h1> | Heading |
| 2 | <p>...</p> | Paragraph |
| 3 | <a>...</a> | Anchor text |
| 4 | <img> | Image |
| 5 | <ol>...</ol> | Ordered list |
| 6 | <ul>...</ul> | Unordered list |
| 7 | <li>...</li> | List items |
| 8 | <br> | Line break |
| 9 | <hr> | Horizontal rule |
| 10 | <b>...</b> / <strong>...</strong> | Bold |
| 11 | <i>...</i> / <em>...</em> | Italic |
| 12 | <sub>...</sub> | Subscript text |
| 13 | <sup>...</sup> | Superscript text |
| 14 | <del>...</del> / <strike>...</strike> | Delete or strikethrough |
| 15 | <mark>...</mark> | Highlight |
| 16 | href | URL |
| 17 | src | path of image |
| 18 | alt | Alternate text |
| 19 | height / width | Height / width |
| 20 | style | Font size, color, etc. |
Thank you for reading! Feel free to react and leave feedback.
